Baking (code generation)
Overview
Out of the box, coherence can use C# Reflection to sync data at runtime. This is a great way to get started but is very costly performance-wise and has a number of limitations on what features can be used through this system.
For optimal runtime performance and a complete feature set, we need to create a schema and perform code generation specific to our project. coherence calls this mechanism Baking.
Learn more about schemas in the How does coherence work section.
How to Bake
Click on the coherence > Bake menu item.
This will go through all indexed CoherenceSync GameObjects (Resources folders and Prefab Mapper) in the project and generate a schema file based on the selected variables, commands and other settings. It will also take into account any LODs that have been added.
For every Prefab with a CoherenceSync component attached, the baking process will generate a C# baked script specifically tuned for it.
Baking settings
Check settings.
When baking, the generated code will output to 📁 Asset/coherence/baked.
You can version the baked files or ignore them, your call.
If you work on a larger game or team, where you use continuous integration, chances are you are better off including the baked files on your VCS.
Since baked scripts access your code, changing networked variables or commands with coherence will get you into compilation errors.
Modifying networked variables or commands - The Watchdog
When you configure your Prefab to network variables, and then bake, coherence generates baked scripts that access your code directly, without using reflection. This means that whenever you change your code, you might break compilation by accident.
For example, if you have a Health.cs script which exposes a public float health; field, and you toggle health in the Configure window and bake, the generated baked script will access your component via its type, and your field via field name.
Like so:
If you decide you want to change your component name (Health) or any of your bound fields (health), Unity script recompilation can fail. In this example, we will be removing health and adding health2 in its place.
When baking via assets, the watchdog is able to catch compilation problems related with this, and offer you a solution right away.
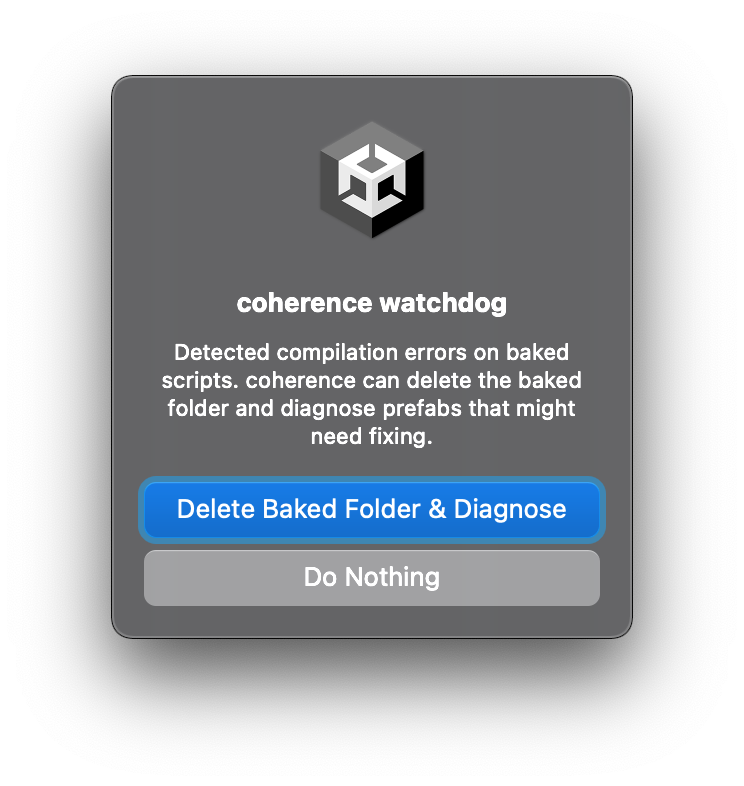
It will suggest that you delete the baked folder, and then diagnose the state of your Prefabs. After a few seconds of script recompilation, you will be presented with the Diagnosis window.
In this window, you can easily spot variables in your Prefabs that can't be resolved properly. In our example, health is no longer valid since we've moved it elsewhere (or deleted it).
From here, you can access the Configure window, where you can spot the problem.

Now, we can manually rebind our data: unbind health and bind health2. Once we do, we can now safely bake again.
Remember to bake again after you fix your Prefabs.
Switching a Prefab to reflection mode
Once the baked code has been generated, Prefabs will automatically make use of it. If you want to switch a particular Prefab to reflection code, you can do so in the Inspector of its CoherenceSync, by unchecking the Baked checkbox:
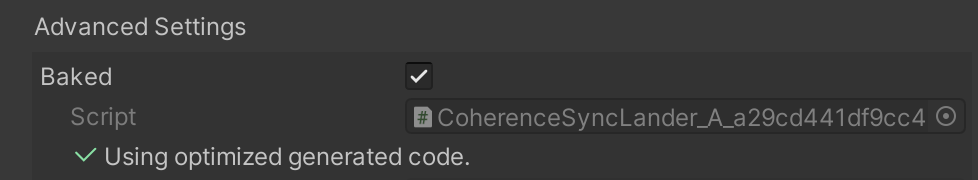
Was this helpful?

