1.2. Animation parameters
Using the same scene as in the previous lesson, let's see how to easily sync animation over the network.
Animation | Bindings
WASD or Left stick: Move character
Hold Shift or Shoulder button left: Run
Spacebar or Joypad button down: Jump
In this scene
We haven't mentioned it before, but the character Prefab does a lot more than just syncing its position and rotation.
When you move around, you will notice that animation is also replicated across Clients. This is done via synced Animator parameters (and Network Commands, but we cover these in the next lesson).
Very much like in the example about position and rotation, just sending these across the network allows us to keep animation states in sync, making it look like network-instantiated Prefabs on other Clients are performing the same actions.
How it's set up
Open the player Prefab located in the /Prefabs/Characters folder. Browse its Hierarchy until you find the child GameObject called Workman. You will notice it has an Animator component.
Select this GameObject and open the Animator window.
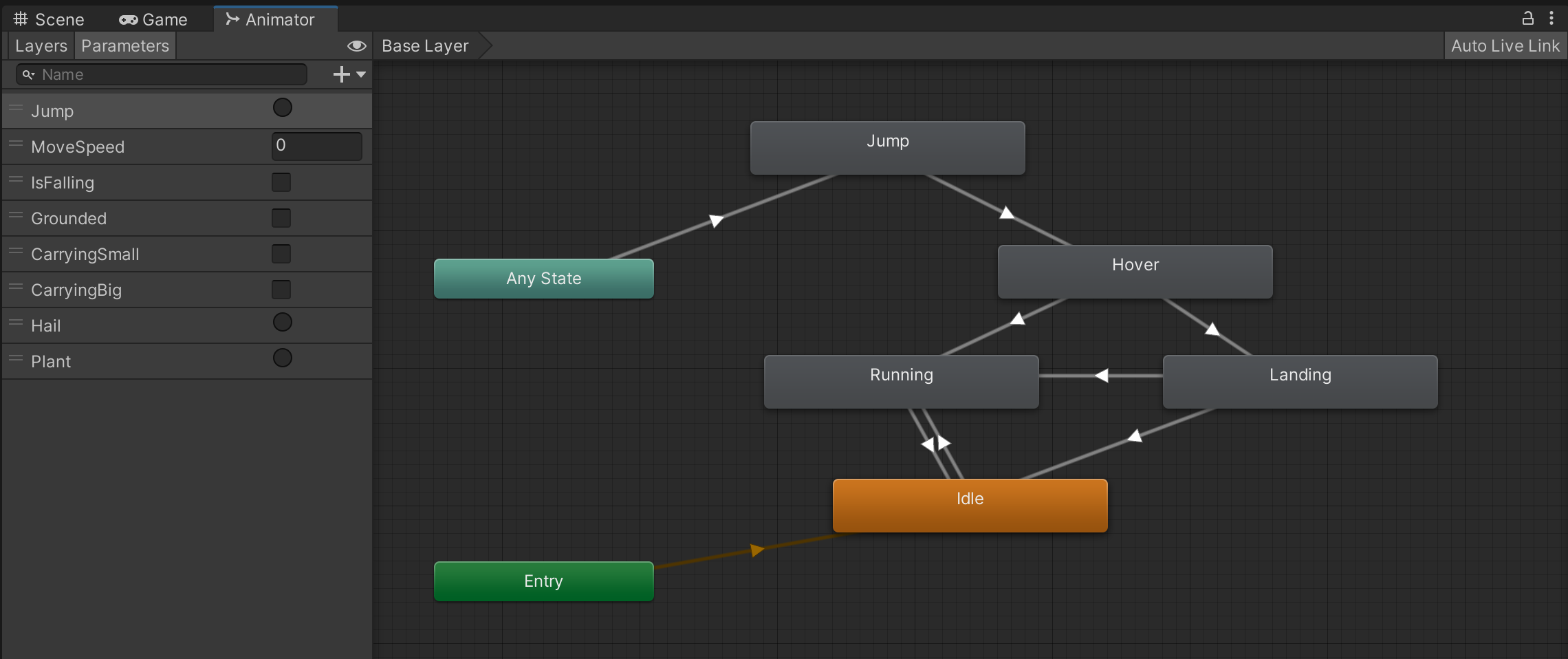
As is usually the case, animation is controlled by a few Animator parameters of different types (int, bool, float, etc.).
Make sure to keep the GameObject with the Animator component selected, and open the coherence Configure window:
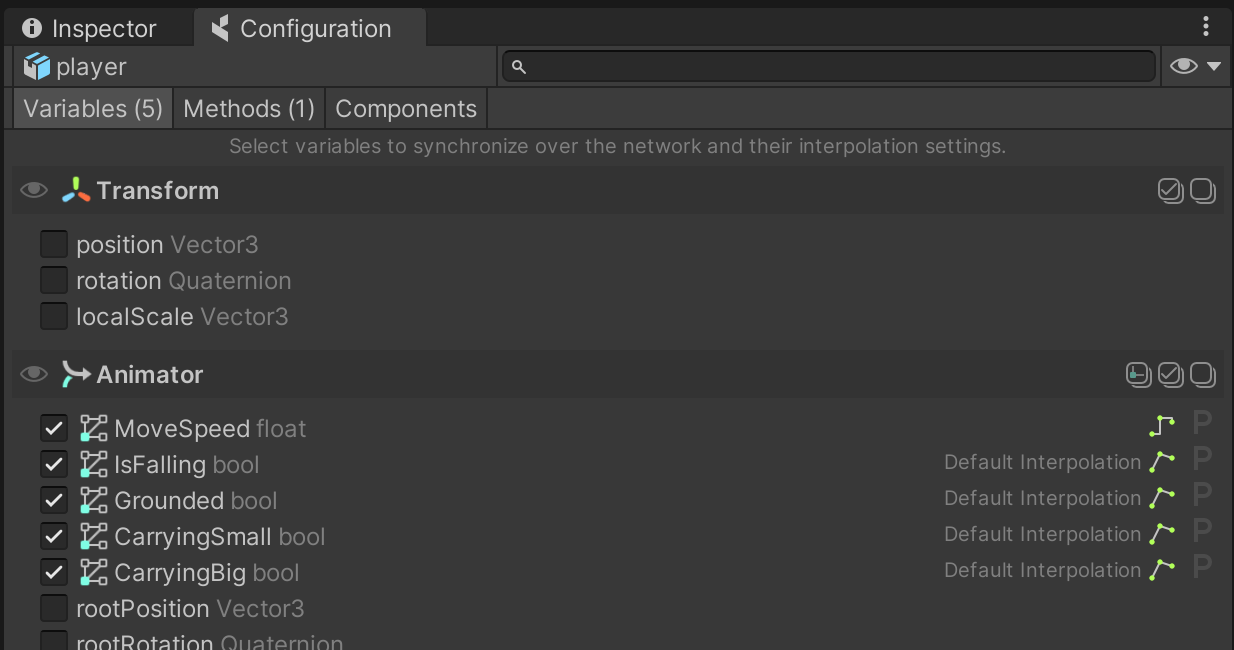
You will see that a group of animation parameters are being synced. It's that simple: just checking them will start sending the values across, once the game starts, just like other regular public properties.
Did you notice that we are able to configure bindings even if this particular GameObject doesn't have a CoherenceSync component on it? This is done via the one attached to the root of the player Prefab.
These parameters on child GameObjects are what we call deep bindings.
Learn more in the Complex hierarchies lesson, or on this page.
There is only one piece missing: animation Triggers. We use one to trigger the transition to the Jump state.
Since Triggers are not a variable holding a value that changes over time, but rather an action that happens instantaneously, we can't just enable in the Config window like with other animator parameters. We will see how to sync them in the next lesson, using Network Commands.
Last updated
Was this helpful?

