2. Physics / Authority transfer
In this sample we look at how to network simple physics simulated directly on the Clients, and the implications of this setup.
If we were making a game that relied on precise physics at play between the players (like a sports match, for instance), we would probably go with a setup where the Clients connect to a Simulator that runs the physics and prevents cheating.
However, that makes running the game much more expensive for the developer, since a Simulator has to be always on.
Physics | Authority transfer | Uniqueness | Persistence
WASD or Left stick: Move character
Hold Shift or Shoulder button left: Run
Spacebar or Joypad button down: Jump
E or Joypad button left: Pick up / throw objects
In this scene
This scene features a few crates that the players can pick up and throw around. Who runs the physics simulation here? You could say that everyone runs their part.
Let's take a closer look at the setup.
How it's set up
Select one of the crates in the scene. You can see that they have normal Box Collider and Rigidbody components. Up until a player is connected, they are being simulated locally. In fact if you press Play, they will fall down and settle.
The crates also have a CoherenceSync component. The first player to connect gets authority over them, and begins simulating the physics for them.
That Client now syncs 5 values over the network, including the most important ones that will drive the crate's motion: Transform.position and Transform.rotation.
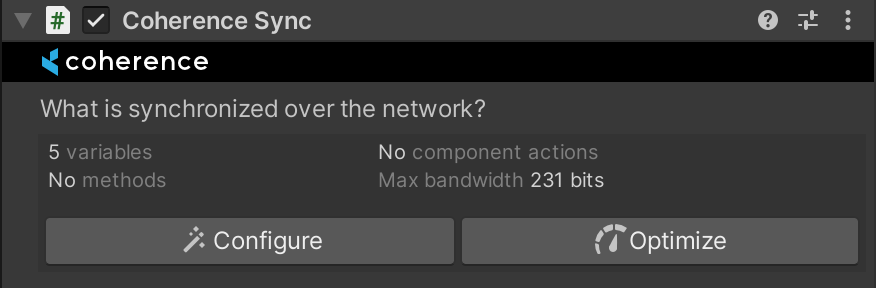
On other Clients however (the ones that connect after the first one) these crates will become "remote". Their Rigidbody will become kinematic, so that now their movement is controlled by the authority (i.e. the first Client).
Authority switch
At this point, the first Client to connect is simulating all the crates. However, if we were to leave things like this, interacting with physical objects that are simulated by another Client would be quite unpleasant due to the lag.
To make it better, other Clients steal authority over crates, whenever they either:
Touch/collide with a crate directly
Pick a crate up
In code, this authority switch is a trivial operation, done in a single line. You can find the code in the Grabbable class. Essentially, it boils down to this:
As you can see, it's good practice to ask first if the requesting script already has authority over an object, to avoid wasted work.
If the request succeeds, the instance of the crate on the requesting Client becomes authoritative, and the Client starts simulating its physics. On the other Client (the previous owner) the object becomes remote (and its Rigidbody kinematic), and is now just receiving position and rotation over the network.
Careful! Since authority request is a network operation, you can't run follow-up code right away after having requested it. It's good practice to set a listener to the events that are available on the Coherence Sync component, like this:
This way, as soon as the reply comes back, we can perform the rest of the code.
Also note that while it's totally possible to configure an object so that Clients can just steal authority from each other, we configured the crates here to require an authority request.
When they want authority, Clients have to request it and most importantly, wait for an answer.
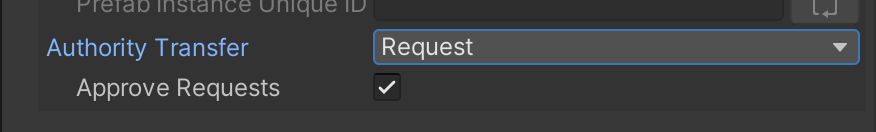
We implemented this request / answer mechanism to avoid problems of concurrency, where two players are requesting authority on a crate at the same time, and end up with a broken state because the game code assumes that they both got it.
In conclusion
So who is running the physics, after all? We can now say that it's everyone at the same time, as roles change all the time.
As we mentioned in the intro - in a simple game where precise physics are non-crucial this might be enough, and it will definitely keep the costs of running the game down, since no Simulator has to run in order to make the game playable.
As mentioned before, pressing Tab (or clicking the Joystick) switches to an authority view. It's very interesting to see how crates switch sides when a player interacts with them.

For more on authority, take a look inside the Grabbable class. It has more code regarding authority events, all commented.
About uniqueness and persistence
There is one important thing to note in this setup. Since the objects are already in the scene at the start, by default every time a Client connects it would try to sync those instances to the network. This is very similar to what we have seen with character instantiation so far: each Clients brings their own copy.
However, in this case this would effectively duplicate the crates, once online. One extra copy for each connected player! We don't want that.
For this reason, the CoherenceSync is configured so that these crates have No Duplicates. This is generally the correct way of configuring networked Prefab instances that have been manually placed in the scene.
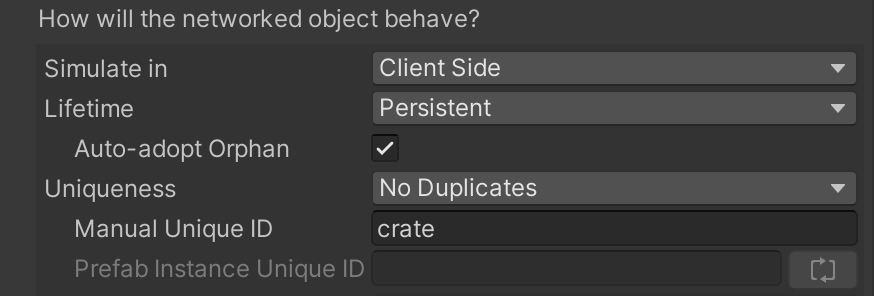
In addition to a unique identifier (the Manual Unique ID), coherence will auto-assign an additional identifier (the Prefab Instance Unique ID) whenever the crate is instantiated in the scene at edit time.
With these parameters in mind, the way the crates behave is as follows:
At the start, none of the entities exist on the Replication Server (yet).
Client A connects. They sync the crates onto the network. Being unique, the Replication Server takes note of their ID.
Client B connects. They try to bring the same crates onto the network, but because it is set to be No Duplicates and coherence finds there is already a network entity with the same ID, it doesn't create a new network entity but recognises that crate as the one on the server, and just makes it non-authoritative for Client B.
If Client A disconnects, the crates are not destroyed because their Lifetime is set to Persistent. They briefly become orphaned (no one has authority on them) but immediately the authority is passed to Client B due to the option Auto-adopt Orphan being on.
For more information on persistence, there's a whole lesson about it.
If everyone disconnects, the crates remain on the Replication Server as network entities that are orphaned. They keep whatever position/rotation they had, since nobody is simulating them anymore.
At this point, nobody is connected. The Replication Server is not doing any work.
When a new Client reconnects and tries to bring the crates online again, the same thing happens again: the crates in the scene are associated with the orphaned entities and are adopted by the new client, who assumes authority on them.
They will also most probably see the crates snap to the last seen position/translation that was stored on the Replication Server, which is synced just before they assume full control over the crates.
At this point, they start simulating their physics locally, like normal.
Was this helpful?

