2. Prefab setup
Preparing GameObjects and Prefabs for network replication
Sync with coherence
To start networking, simply select a Prefab or GameObject you wish to network, and on the Inspector window, click Sync with coherence.
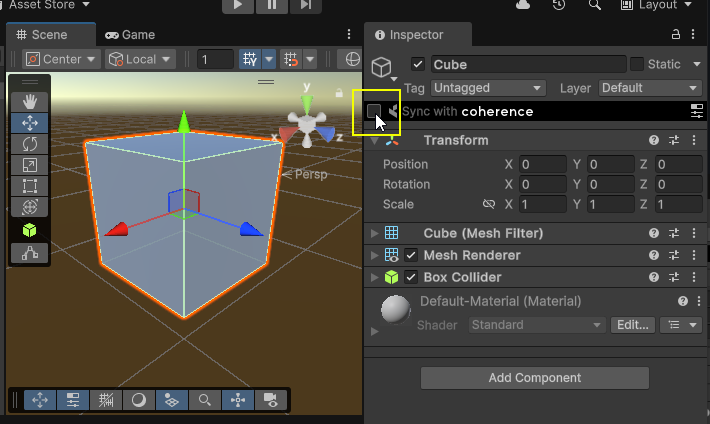
Now, your Prefab should have a CoherenceSync component attached to it.
To select which properties you want to network, open the Configure window, accessible from within the CoherenceSync Inspector.
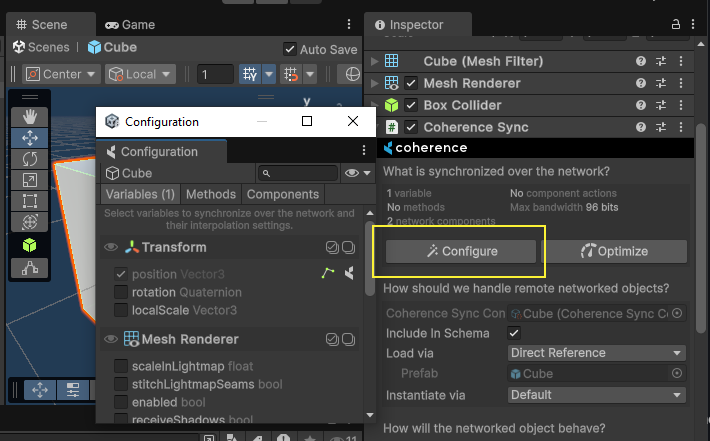
When new Networked Prefabs are included, or the properties to network are changed, you will need to Bake and make sure the Replication Server (either local or the one in the Cloud) is using the schema generated afterwards.
Video Tutorial
Setting up basic syncing is explained in this video, from 1:00 and onwards:
Detailed Step by Step
1. Add CoherenceSync component
CoherenceSync componentFor an object to be networked through coherence, it needs to have a CoherenceSync component attached, and be a Prefab.
The steps below all do this, but from different starting points: a new GameObject (1a), a pre-existing Prefab (1b), or a Prefab Variant (1c).
Currently, only Prefabs can be networked.
1a. To a new GameObject
First, create a new GameObject. In this example, we're going to create a cube.
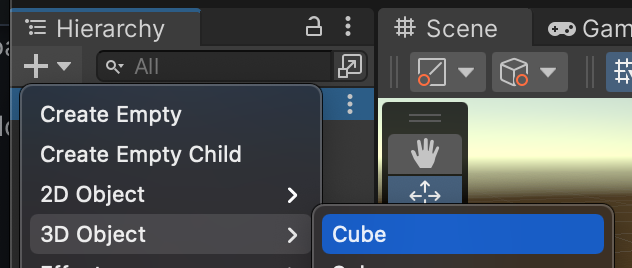
Next, we add the CoherenceSync component to Cube.
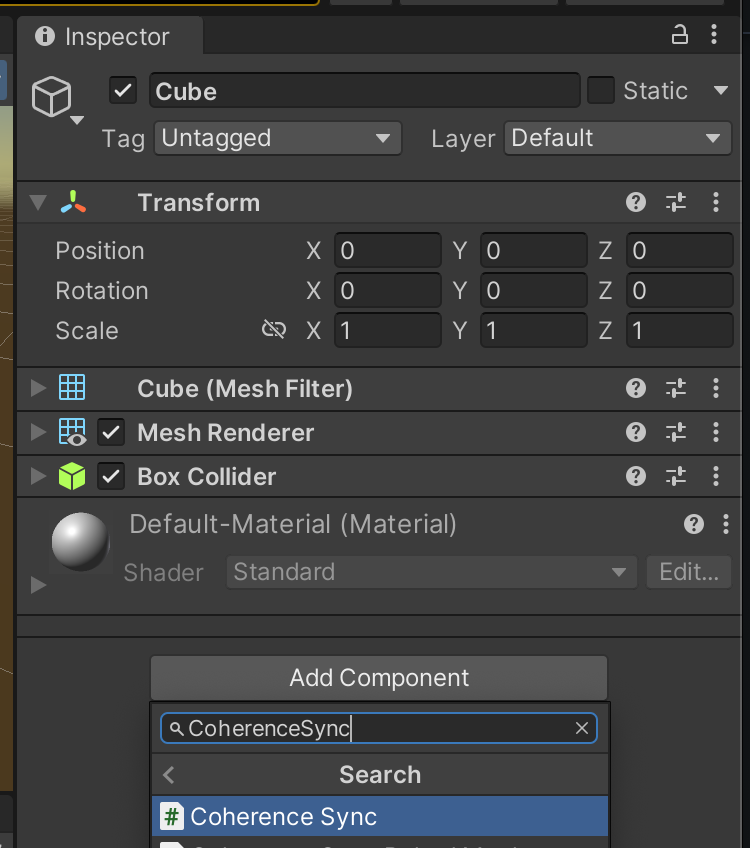
The CoherenceSync inspector now tells us that we need to make a Prefab out of this GameObject for it to work. We get to choose where to create it:
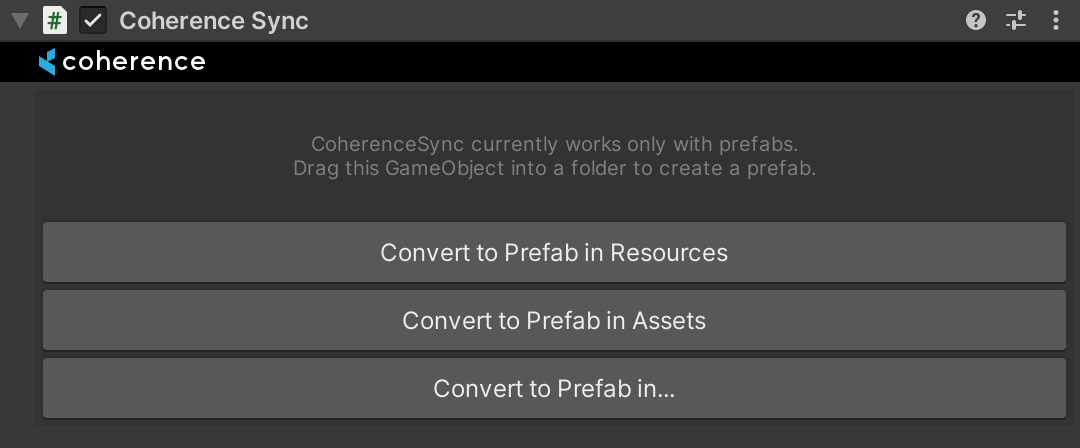
1b. To an already existing Prefab
First, ensure you enter Prefab mode, as we don't want to add the component as an override.
Ensure you're in Isolation Prefab editing mode, not In Context. Read about Prefab modes.
Now you can either:
Click on the Sync with coherence checkbox at the top of the Prefab inspector.
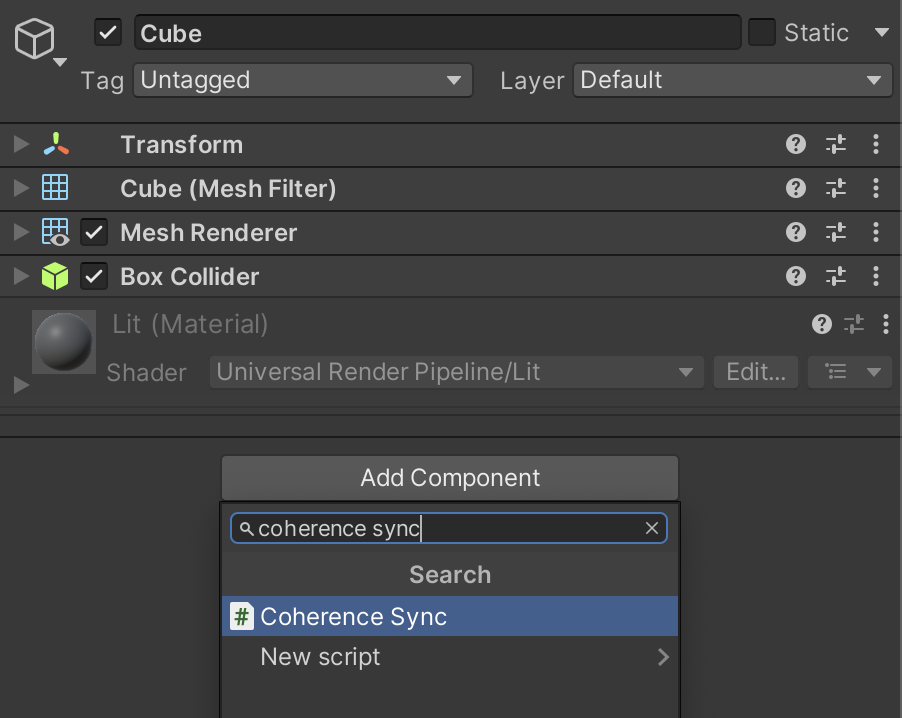
Manually add the
CoherenceSynccomponent.
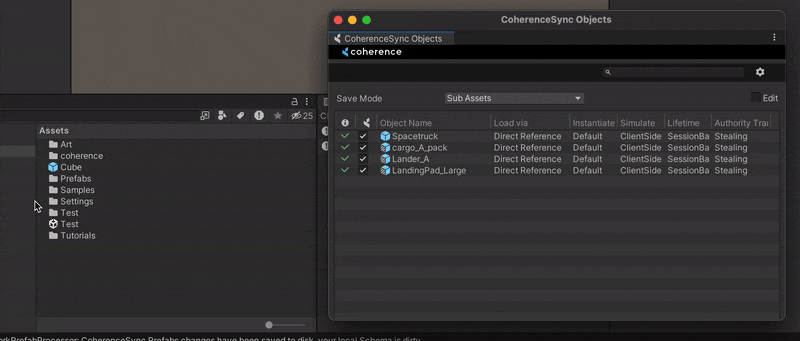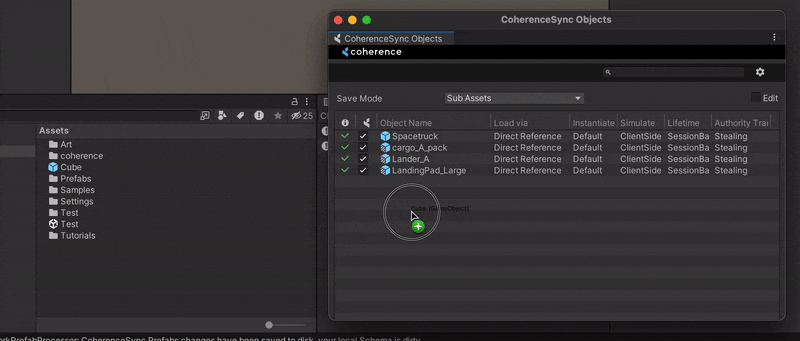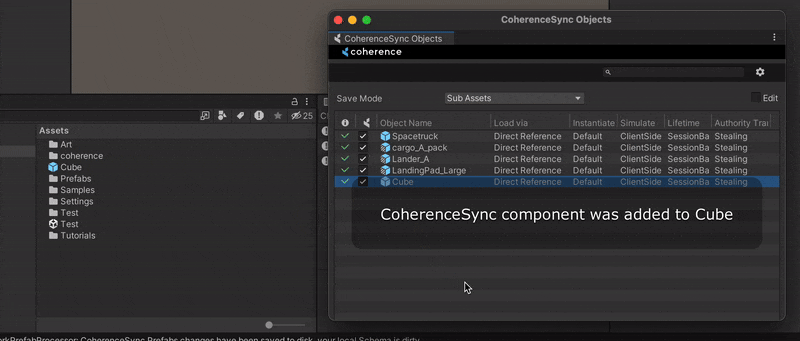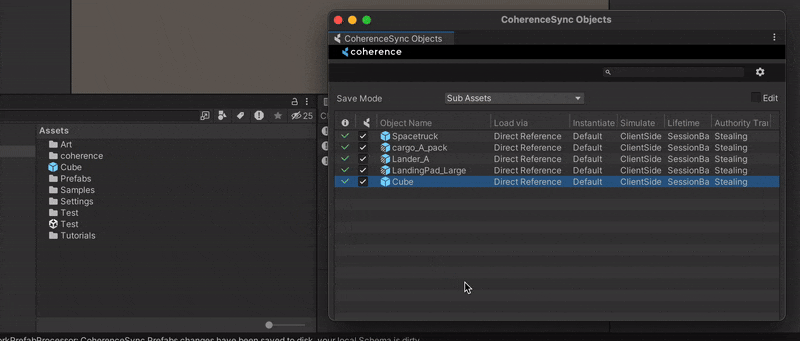
Drag the Prefab to the CoherenceSync Objects window. You can find it in coherence > CoherenceSync Objects.
1c. Prefab variants
One way to configure a pre-existing Prefab for networking, instead of just adding CoherenceSync to it, is to derive a Prefab variant and add the component to that instead.
In our Cube example, instead of adding CoherenceSync to Cube, you can create a Cube (Networked) Prefab and add the component to it:
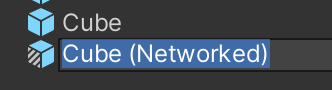
This way, you can retain the original Prefab untouched, and build all the network functionality separately, in its own Prefab.
Ensure you're in Isolation Prefab editing mode, not In Context. Read about Prefab modes.
Learn how to create and use Prefab variants in the Unity Manual.
Another way to use Prefab variants to our advantage is to have a base Prefab using CoherenceSync, and create Prefab variants off that one with customizations.
For example, Enemy (base Prefab) and Enemy 1, Enemy 2, Enemy 3... (variant Prefabs, using different models, animations, materials, etc.). In this setup, all of the enemies will share base networking settings stored in CoherenceSync, so you don't have to manually update every one of them.
The Prefab variants inherits the network settings from their base, and you change those with overrides in the Configuration window. When a synced variable, method or component action is present in the variant and not in the parent, it will be bolded and it will have the blue line next to it, just like any other override in Unity:
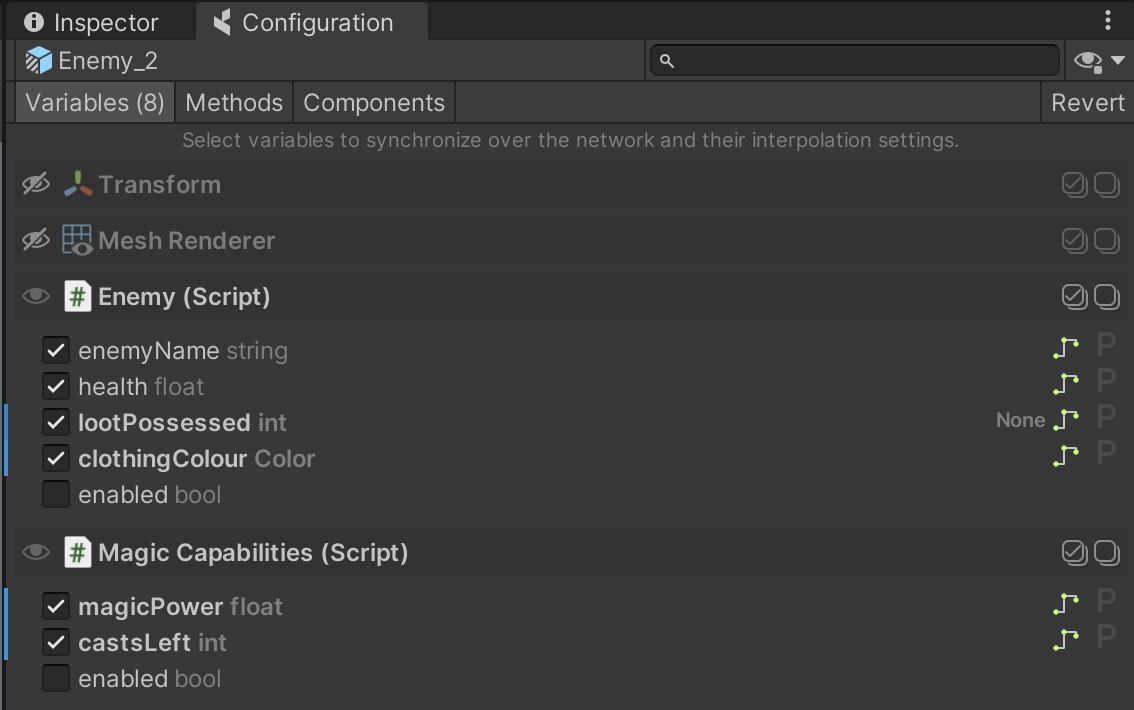
2. Configure CoherenceSync
CoherenceSyncThe CoherenceSync component will help you prepare an object for network synchronization during design time. It also exposes APIs that allow to manipulate the object during runtime.
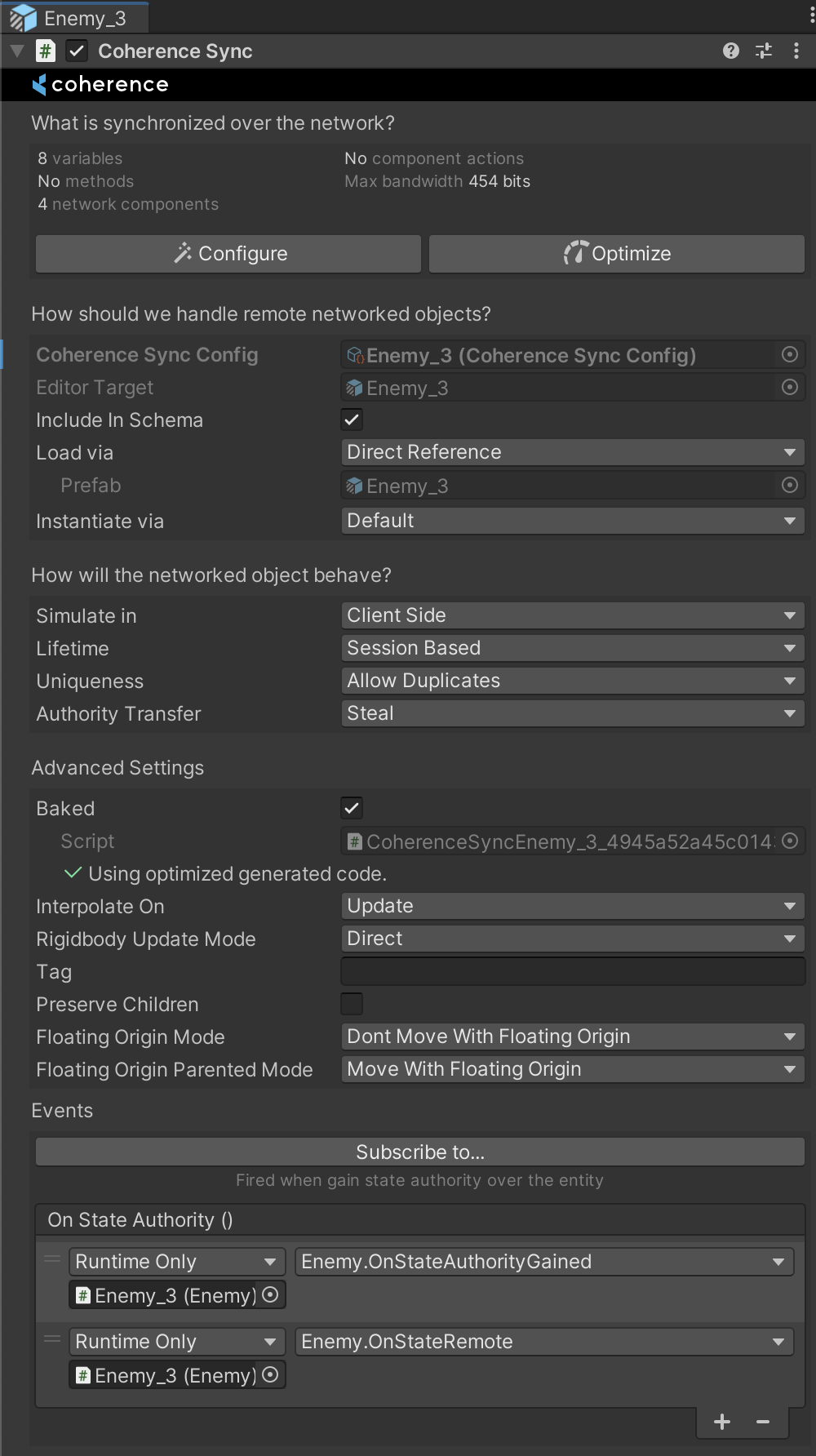
In its Inspector you can configure settings for Lifetime (Session-based or Persistent), Authority transfer (Not Transferable, Request or Steal), Simulate In (Client-side, Server-side or Server-side with Client Input) and Adoption settings for when persistent entities become orphaned, and more.
There are also a host of Events that are triggered at different times.
Its Inspector has quite a number of settings. For more information on them, refer to the CoherenceSync page.
For now, we can leave these settings to their defaults.
2.1. Select variables to replicate
CoherenceSync allows you to automatically network all public variables and methods on any of the attached components, from built-in Unity components such as Transform, Animator , etc. to any custom script, including scripts that came with the Asset Store packages that you may have downloaded.
Make sure the variables you want to network are set to public. coherence cannot sync non-public variables.
To set it up, click on the Configure button in the CoherenceSync's Inspector. This brings up the Configuration window. Here you can select which variables you would like to sync across the network:
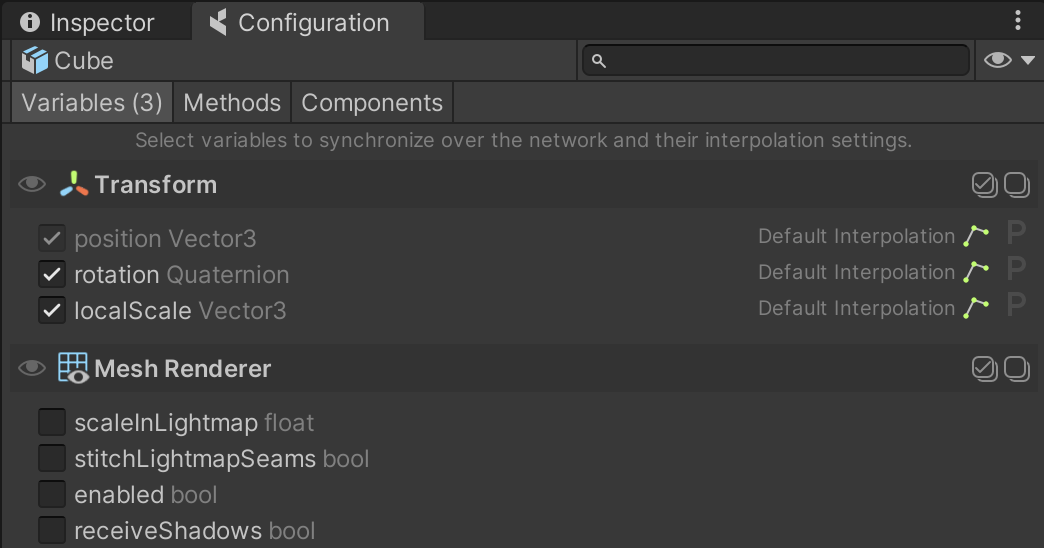
You will notice that position is already selected, and can't be unchecked. For our use case, let's also add rotation and localScale.
Close the Configuration dialog.
Note that you can configure variables, methods and components not only on the root, but also on child GameObjects.
3. Add a script
Let's add a simple movement script that uses WASD or Arrow keys to move the Prefab in the scene.
Click on Assets > Create > C# Script. Name it Move.cs.
Copy-paste the following content into the file:
Wait for Unity to compile, then attach the script to the Prefab.
4. Disable components on replicated objects
We have added a Move script to the Prefab. This means that if we just run the scene, we will be able to use the keyboard to move the object around.
But what happens with Prefab belonging to other Clients? We don't have authority over them, they just need to be replicated. We don't want our keyboard input interfering with them, we just want the position coming from the network to be replicated.
For this reason, we need the Move component to be disabled when the object is remote. coherence has a quick way to do this.
In the Configuration window, click the Components tab:
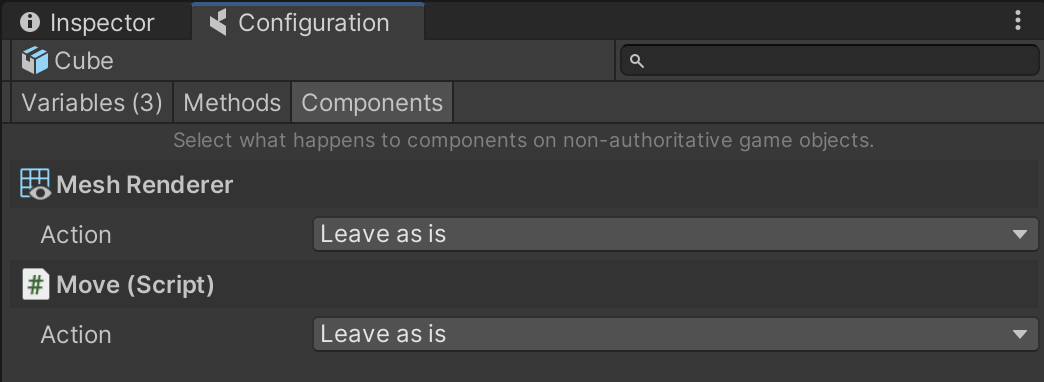
Here you will see a list of Component Actions that you can apply to non-authoritative entities that have been instantiated by coherence over the network.
Selecting Disable for your Move script will make sure the Component is disabled for network instances of the Prefab:
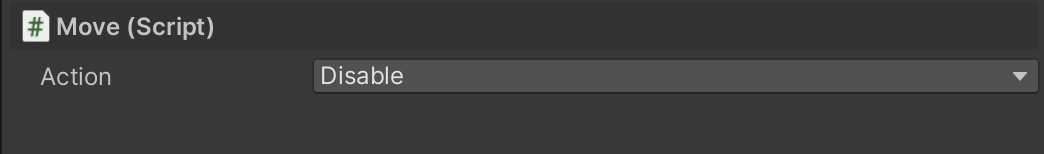
This ensures that if a copy of this Prefab is instantiated on a Client with no authority, this script will be disabled and won't interfere with the position that is being synced.
5. Bake the netcode
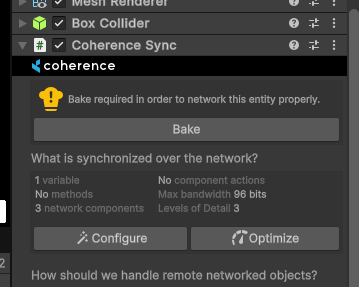
Once everything is setup, you should ensure to run the process of Baking: coherence will produce the necessary netcode (i.e. a bunch of C# scripts) to ensure that when the game is running and the Client connects, all of the properties and network messages you might have configured will correctly sync.
This process is very quick, and can be done in different ways:
From the menu item coherence > Bake
From the icon next to the coherence folder in the Project Window
From the Hub
From a CoherenceSync
To recap
This is it! Setting up an object to be networked doesn't require additional steps:
A Prefab with a
CoherenceSyncon itConfiguring what to sync in the Configure window
Disabling components on remote entities, in the Configure > Components tab
Baking the netcode
Now let's run this setup locally or using the coherence cloud.
Was this helpful?

