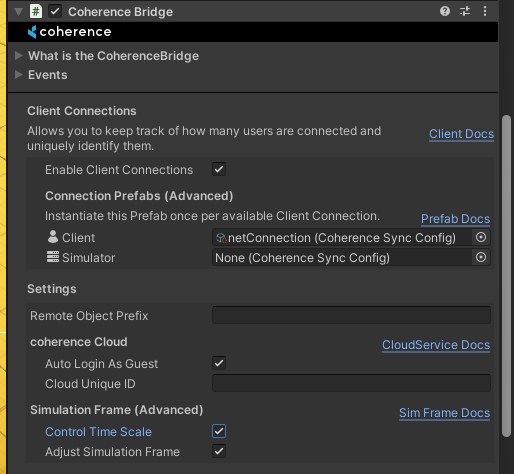
Simulation Frame
Simulation Frame
void Start()
{
if (!CoherenceBridgeStore.TryGetBridge(gameObject.scene, out var bridge))
{
Debug.LogWarning("Couldn't find CoherenceBridge in the scene.");
return;
}
var networkTime = bridge.NetworkTime;
var serverFrame = networkTime.ServerSimulationFrame.Frame;
Debug.Log("Server Simulation Frame: " + serverFrame);
var clientFrame = networkTime.ClientSimulationFrame.Frame;
Debug.Log("Client Simulation Frame: " + clientFrame);
}
Client fixed simulation frame
Was this helpful?

