Scripting: Client vs Simulator
When scripting Simulators, we need mechanisms to tell them apart.
Am I a Simulator ?
using Coherence;
using UnityEngine;
public class SimulatorClass : MonoBehaviour
{
public void Awake()
{
if (SimulatorUtility.IsSimulator)
{
// I'm a simulator!
}
}
}Connect and ConnectionType
Connect and ConnectionTypeCOHERENCE_SIMULATOR
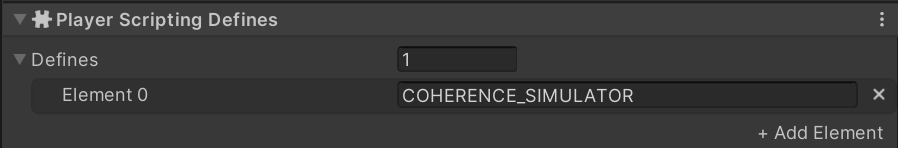
Command-line argument
Server-side simulation
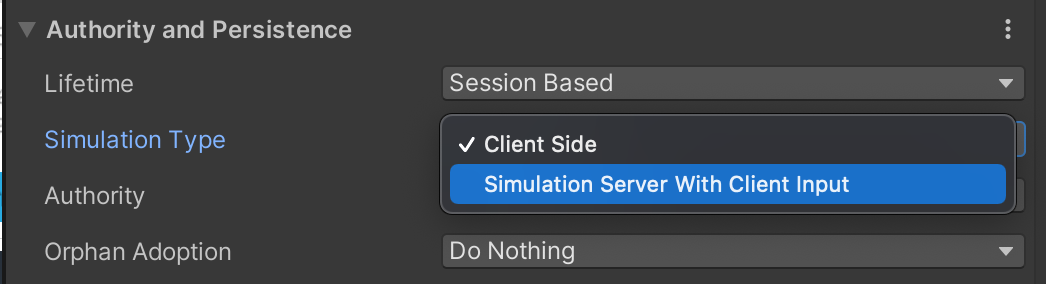
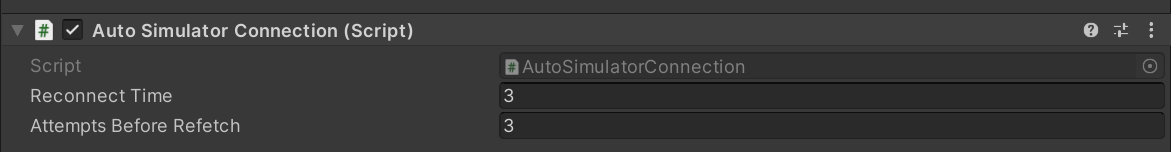
Connecting Simulators automatically to RS: AutoSimulatorConnection Component
Was this helpful?

