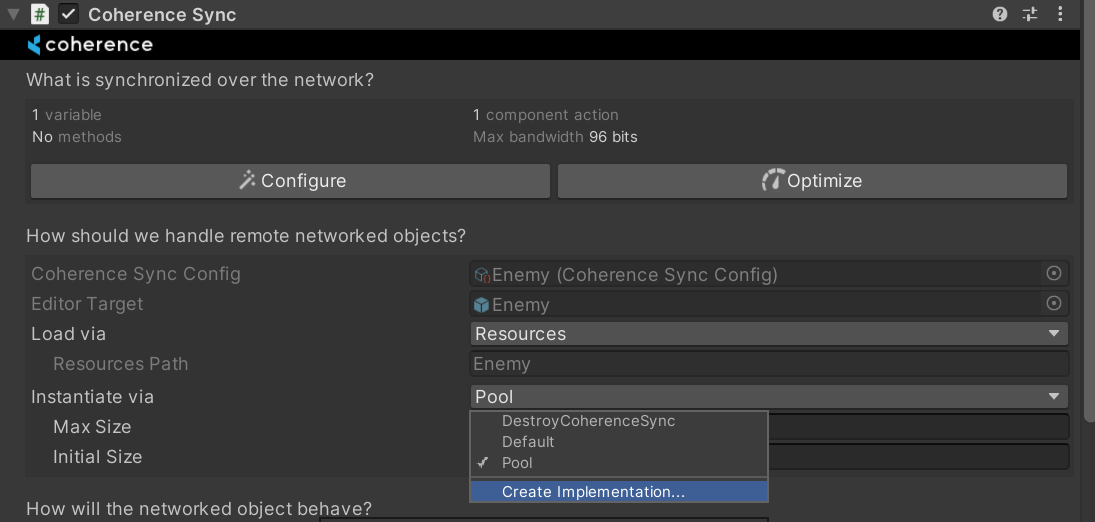
Instantiate via
In coherence, it is possible to specify how a Prefab is instantiated at runtime using the Instantiate via option on the CoherenceSync.
We support three default implementations, or you can create your own. The three default implementations are Default, Pooling or DestroyCoherenceSync.
Default Instantiator
This instantiator will create a new instance of your prefab, and when the related network entity is destroyed, this prefab instance will also be destroyed.
Pool Instantiator
This instantiator supports object pooling, instead of always creating and destroying instances, the pool instantiator will attempt to reuse existing instances. It has two options:
Max Size: maximum size of the pool for this prefab, instances that exceed the limit of the pool will be destroyed when returned.
Initial Size: coherence will create this amount of instances on app startup.
DestroyCoherenceSync Instantiator
This instantiator will create a new instance for your prefab, but instead of completely destroying the object when the related network entity is destroyed, it will destroy or disable the CoherenceSync component instead.
Creating your own instantiator
You can implement the INetworkObjectInstantiator interface to create your custom implementations that will be used by coherence when we need to instantiate a pefab in the scene.
Custom implementations can be Serializable and have your own custom serialized data.
Implementations of this interface will be automatically selectable via the Instantiate via option in the CoherenceSync for the object, or on the corresponding CoherenceSyncObject asset.
Last updated
Was this helpful?

