Game mechanics
Before we dive into the networking-specific topics, in this introductory page we'll quickly go over how the whole gameplay is structured and set up. We'll cover it both from a point of view of Prefabs and of code so you know where to look for what.
Controls
WASD: Move | Shift: Sprint | Spacebar: Jump | E: Pick up/throw, Chop trees, Sit/stand | C: Random appearance | 1: Wave emote | 2: Dance | 3: Yes emote | 4: No emote | Enter: Show chat/send message | Esc: Cancel chat
Left stick: Move | Left trigger: Sprint | Button south: Jump | Button west: Pick up/throw, Chop trees, Sit/stand | Button east: Random appearance | D-pad up: Wave emote | D-pad down: Dance | D-pad left: Yes emote | D-pad right: No emote | Select button: Show/hide chat | Start button: Send chat
Player characters, interactions
You'll find the Player Prefab in 📁Prefabs/Characters.
When connecting, an instance of the Player is instantiated in the scene by the PlayerHandler script, which listens to the corresponding event fired by CoherenceBridge.
The player character is a Rigidbody-driven kinematic capsule that is hovering above the ground slightly, and detecting the ground via a raycast. Movement values are provided by the Move script on its root, which is in turn informed by the PlayerInput component. When instantiated over the network both these components are disabled, and the Rigidbody is set to be kinematic.
Besides movement, other actions are controlled by scripts on three child GameObjects: Interactions, Emotes, and Chat.
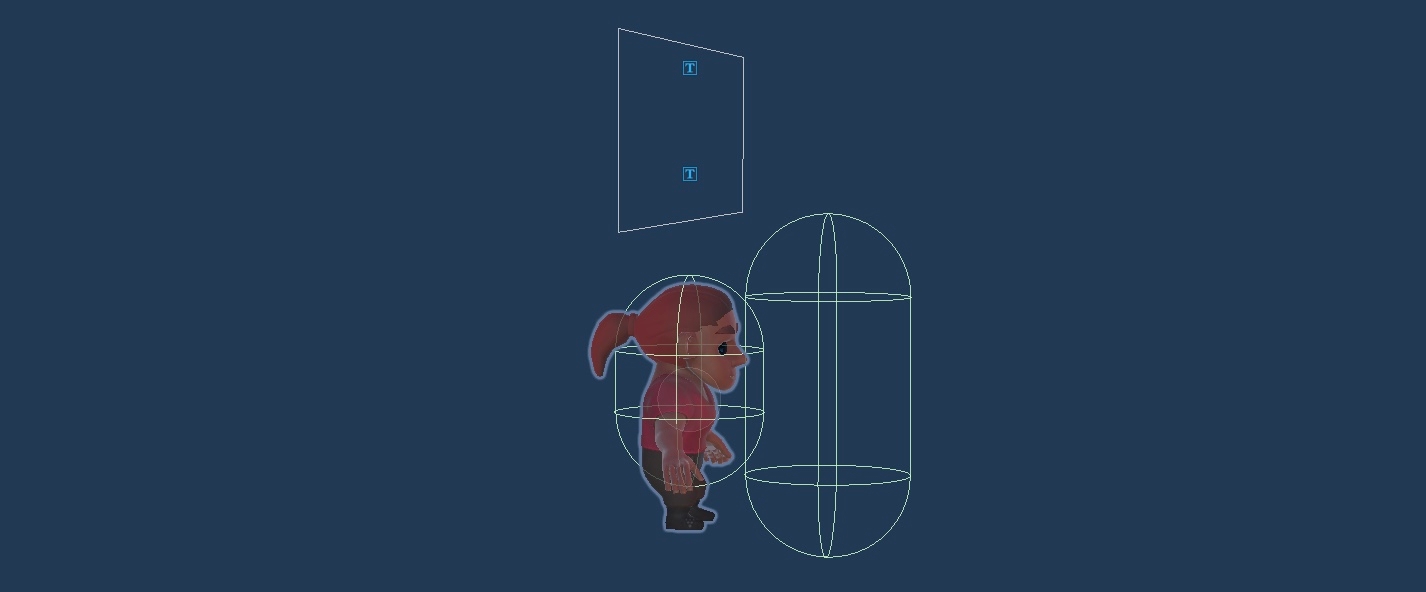
When approaching an object that can be interacted with, the InteractionInput script does the work of detecting objects that have an Interactable script, and highlights them by changing their layer. This makes them render with an additional outline, as per one of the passes in the URP Renderer Renderer_WorldUI, contained in 📁Settings.
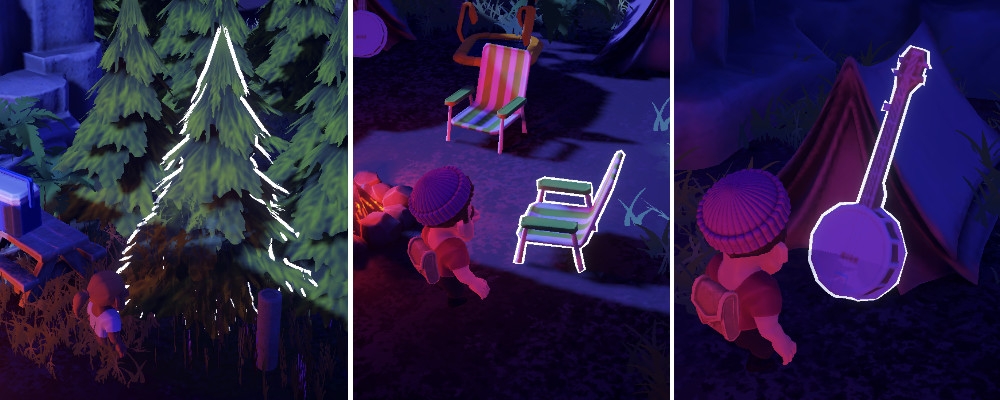

When pressing the interaction key, the right action will be carried on by one of the scripts ChopAction, SitAction, and GrabAction, depending on the type of the object highlighted (a ChoppableTree, a Chair, or a Grabbable).
The chat system is described here. Other actions are described below.
The Player Prefab builds on the structure and functionality of the one used in the First Steps tutorial project, adding more actions. If you find it complex to dive into, try exploring that version first.
Chopping down trees
The prefab for the interactive tree is in 📁Prefabs/Interactive. The log that is spawned by it is in 📁Prefabs/Interactive/Burnables.
The trees have an Interactable script that indicates which mesh gets highlighted.
They have an amount of energy that determines the number of times they need to be chopped to be cut down. When they run out, they transition to a chopped state and spawn a tree log. A coroutine makes them spring out again after a certain amount of time.
Read more about how characters interact with remote trees in this page about dealing with a non-authority object.
The campfire
The campfire Prefab is in 📁Prefabs/Interactive.
The campfire is at the center of this demo. Players can burn anything they can pick up by simply throwing the object into it. The campfire exists only in one instance and is pre-placed in the scene, and marked as unique on the network by setting the Uniqueness property of its CoherenceSync to No Duplicates.
Most of the logic of the campfire is in the Campfire component. This handles a lot of the networking flow, and can be run by a Client but, if a Simulator connects, they will take over.
In addition to calculating which fire effect to display, it's also in charge of replicating the sound of burning an object on all Clients (read more about effects here).
Learn more about the campfire's logic on this page.
Carrying and burning objects
All non-static interactive objects are in 📁Prefabs/Interactive/Burnables.
They are all Prefab Variants of a base Prefab called Base_BurnableObject, which you can inspect to get a sense of the common functionality.
The objects have several scripts: Grabbable provides the ability for them to be picked up, carried and thrown, while Burnable grants the ability to be burnt on the campfire.
They have a collider at the root which determines collisions, but a child GameObject named Interaction (and its Interactable script) has the trigger collider that makes it interactive, and allows to pick the object up. The Interactable script also holds a reference to the objects to highlight when the player's interaction trigger intersects the object.
Burnable types

The logs that are spawned when chopping down trees are not unique, and they are set to Allow Duplicates. Check this page for more info on the logs and how they are recycled using an object pool.
Instead, the other burnable objects are pre-placed in the scene, and set to be unique (No Duplicates): the banjo, the cooler, the bins, the mushrooms, and more. More details on the lifetime of these pre-placed objects in the section below.
The server-side Keeper Robot
You'll find the robot Prefab in 📁Prefabs/Characters.
The Keeper Robot is an NPC designed to be run by a Simulator (aka, the "server"), to restore the campsite to its initial state even when no-one is connected.
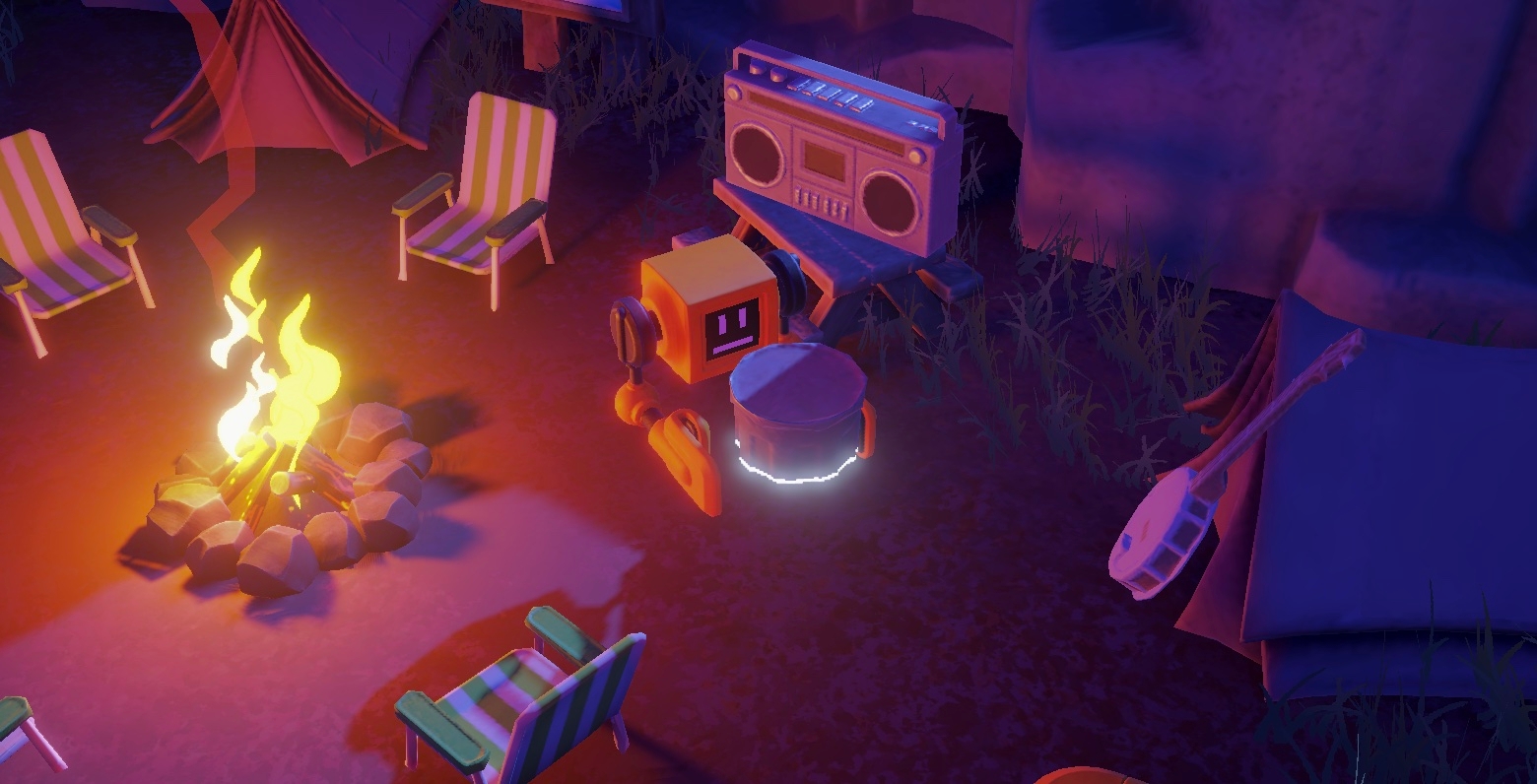
Its script will cycle through all unique campfire objects every X seconds. If an object has been destroyed, it will recreate it and put it in its place. If it has been moved, it will just chase it down and put it back into its place.
The way the robot knows about destroyed objects is because the objects, when created the first time, spawn an invisible marker (that we call an "object anchor") which the robot can inspect to know which object has disappeared, and where it was originally placed. The page about custom instantiation has more info on these objects and their anchors.
Read more about this server-side NPC works on its dedicated page.
Chairs and sitting
You will find chairs in 📁Prefabs/Interactive/Chairs.

Sitting is one of the three actions that can be performed by interacting with objects. It doesn't have networking effects, so it's not covered in this tutorial pages.
Was this helpful?

