Multi-Room Simulators
Simulate multiple Rooms at the same time, within one Unity instance
Multi-Room Simulators are Room Simulators which are able to simulate multiple game rooms at the same time - one sim to rule them all!
In order to achieve this, the game code should be defensive on which room it is affecting. Game state should be kept per Room, meaning game managers, singletons (static data), etc. need to account for this.
Each Room is held in a different scene. So for every Room created, the Multi-Room Simulator should open a connection to it, hence loading additively a scene and stablishing a Simulator connection (via Bridge).
How do they work?
By using Multi-Room Simulators, the coherence Cloud is able to instruct your Simulator which room to join and start simulating.
This communication happens via HTTP. An HTTP server is started by your game build when the MultiRoomSimulator component is active. This component listens to HTTP requests made by the coherence __ Online Dashboard.
For offline local development, you can use a MultiRoomSimulatorLocalForwarder component on your clients, which will create HTTP requests against your local simulator upon client connection, like joining a room.
For local development, enable the Local Development Mode flag in the project settings.
Once the MultiRoomSimulator receives a request to join a room, it spawns a CoherenceSceneLoader that will be in charge of loading additively the scene specified.
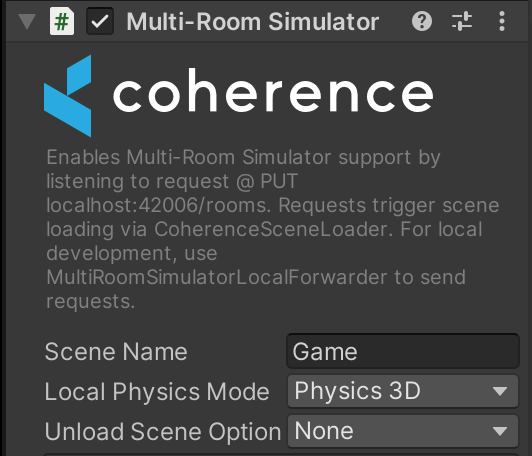
By default, scenes will have their physics scene. coherence ticks the physics scene on the CoherenceScene component, which the target scene to be loaded should include.
Setting up Multi-Room Simulators
The quickest way to get Multi-Room Simulators set up is by using the provided wizard.
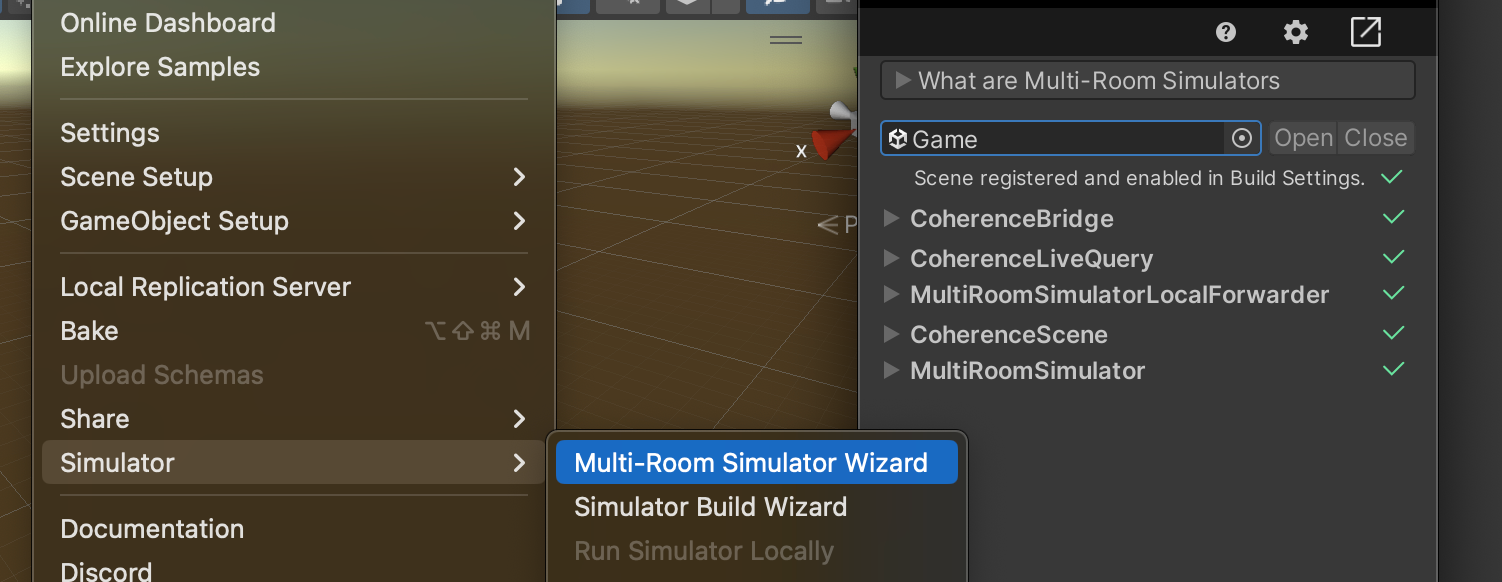
It will take you through the GameObjects and Components needed to make it happen.
Manually setting up Multi-Room Simulators
Here's a quick overview video of the setup:
These are the pieces needed for Multi-Room Simulators to work:
Simulators
In the initialization scene (splash, init, menu, ...)
MultiRoomSimulator — listens to join room requests and delegates scene loading (by instantiating CoherenceSceneLoaders)
Clients
(Only for local development) In the scene where you connect to a Room (where you have the Sample UI or your custom connection logic)
MultiRoomSimulatorLocalForwarder — requests the local MultiRoomSimulator to join rooms when the Client connects.
Independently
In the scene where the networked game logic is (game, Room, main, ...)
Bridge — handles the connection
LiveQuery — filters Entities by distance
CoherenceScene — when the scene is loaded via CoherenceSceneLoader, it will try to connect using the data given by it. It attaches to the Bridge, creates a connection, and handles auto reconnection. If a scene loaded through CoherenceSceneLoader doesn't have a CoherenceScene on it, one will be created on the fly.
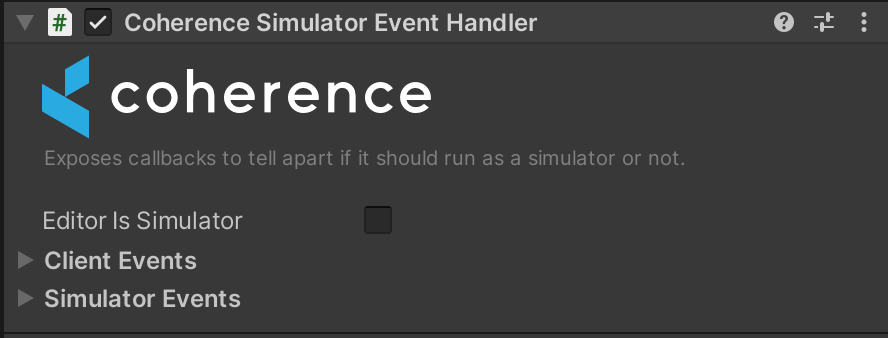
There are two components that can help you fork Client and Simulator logic, for example, by enabling or disabling the MultiRoomSimulator component depending on whether it's a Simulator or a Client build. These are optional but can come in handy.
SimulatorEventHandler — events on the build type (Client/Simulator).
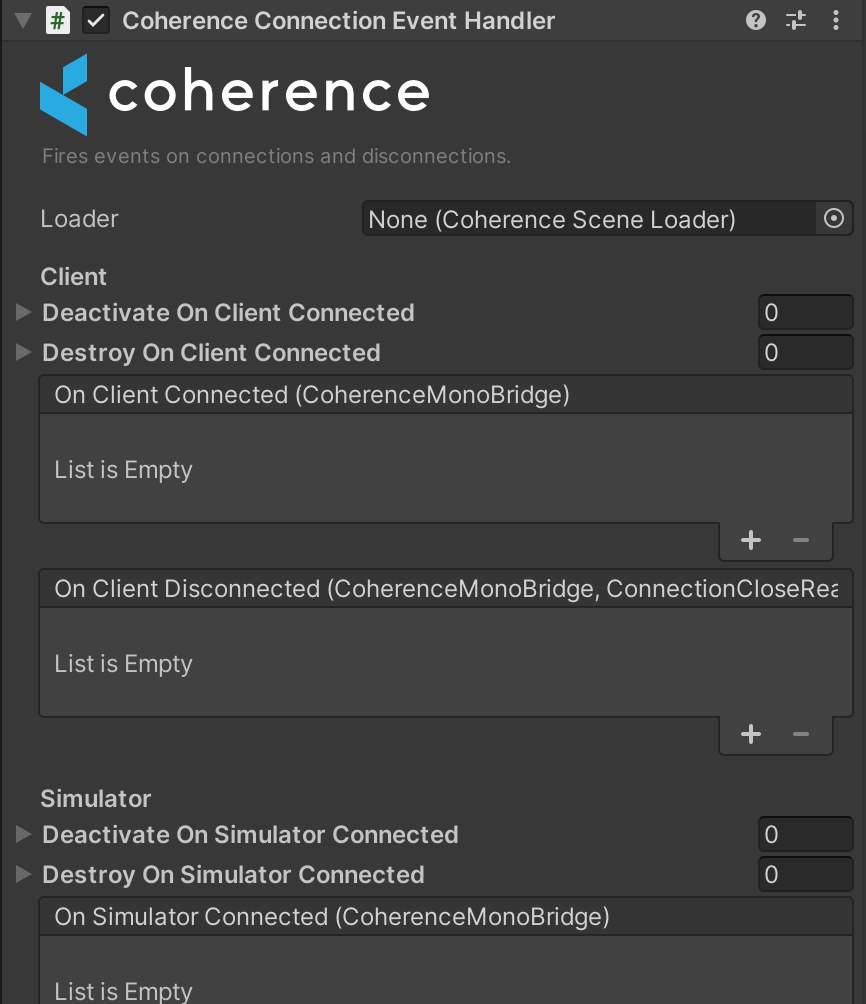
ConnectionEventHandler — events on the connection stablished by the Bridge associated with that Scene.
In-editor debugging
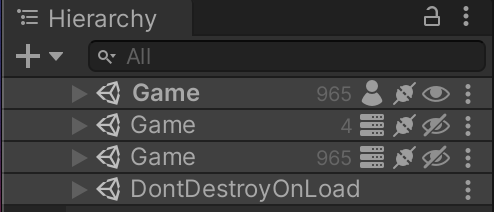
It is possible to visualize each individual Room the Multi-Room Simulator is working on. By default, Simulator connections to Rooms are hidden, as shown in the image above. You can toggle the visibility per scene by clicking the Eye icon. You can also change the default visibility of the loaded scene (defaults to hidden) on the CoherenceScene component:
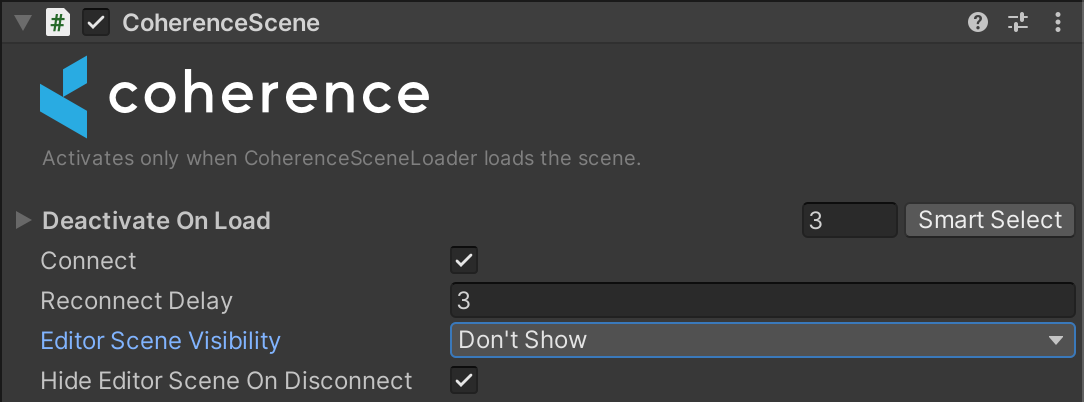
Limitations
Working with Multi-Room Simulators needs your logic to be constrained to the scene. Methods like FindObjectsOfType will return objects in all scenes — you could affect other game sessions!
Check out Coherence.Toolkit.SceneUtils for alternative APIs to FindObjectsOfType that work per scene.
Also, Coherence.Toolkit.ActiveSceneScope can help make sure instantiation happens where you want it to be.
This is also true for static members, e.g. singletons. When using Multi-Room Simulators, there need to be as many isolated instances of your managers as there are open simulated rooms.
For example, if you were to access your Game Manager through GameManager.instance, now you'll need a per-scene API like GameManager.GetInstance(scene).
There may be third-party or Unity-provided features that can't be accessed per scene, and that affect the whole game.
Loading operations, garbage collections, frame-rate spikes... all these will affect performance on other sessions, since everything is running within the same game instance.
Allowing Multi-Room Simulators in the Online Dashboard
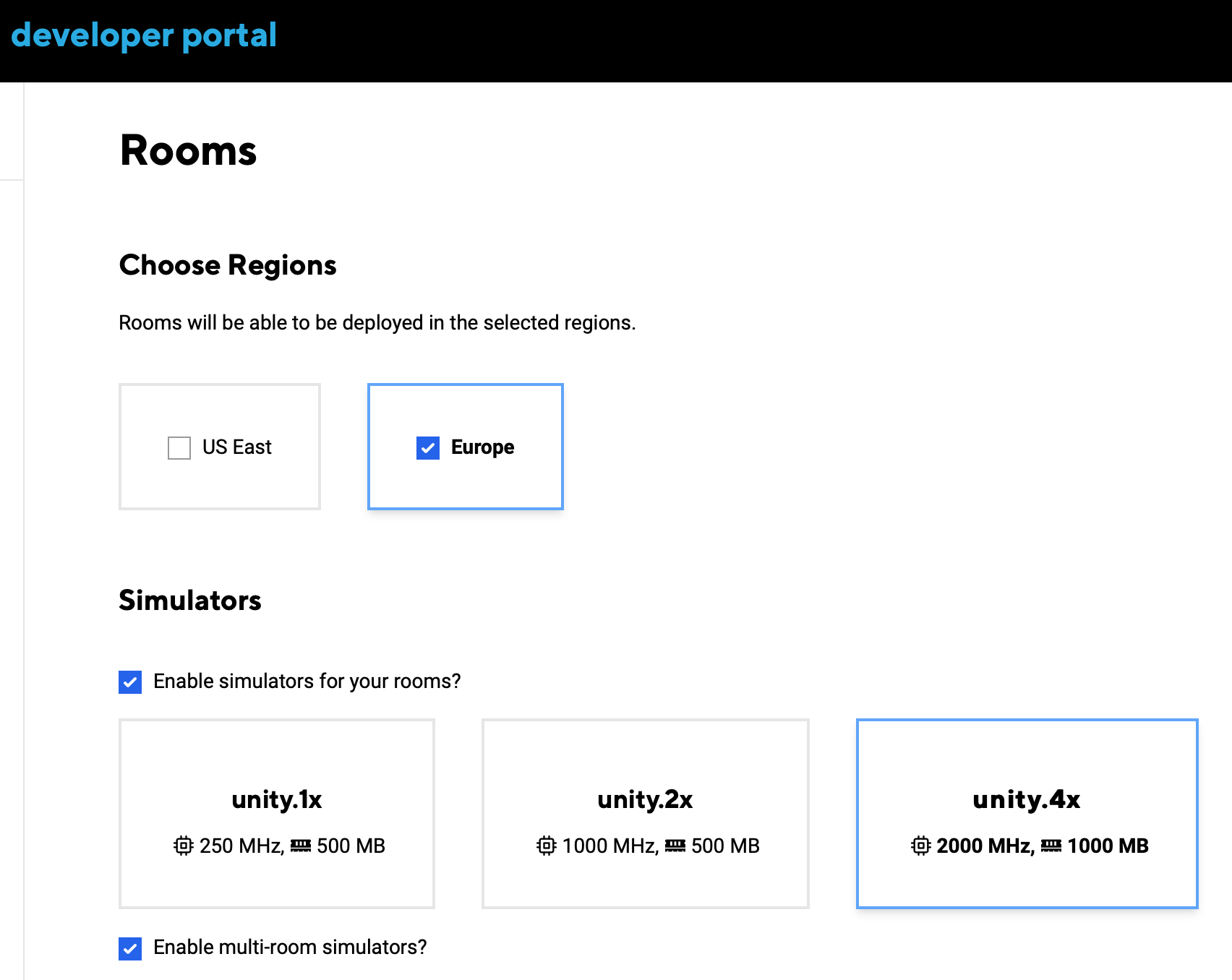
Multi-Room Simulators are still Room Simulators. You need to enable Simulators for Rooms and enable Multi-Room Simulators in the coherence Online Dashboard, as shown here:
Was this helpful?

