1.2 Sending commands
Using the same scene as in the previous lesson, we now take a look at another way to make Clients communicate: Network Commands. Network Commands are commonly referred to as "RPCs" (Remote Procedure Calls) in other networking frameworks. You can think of them as sending messages to objects, instead of syncing the value of a variable.
WASD or Left stick: Move character
Hold Shift or Shoulder button left: Run
Spacebar or Joypad button down: Jump
Q or D-pad up: Wave
In this scene
Building on top of previous examples, let's now focus on two key player actions. Press Space to jump, or Q to greet other players. For both of these actions to play their animation, we need to send a command over the network to invoke Animator.SetTrigger() on the other Client.

How it's set up
Like before, select the player Prefab located in the /Prefabs/Characters folder, and browse its Hierarchy until you find the child GameObject called Workman.
Open the coherence Configure window on the third tab, Methods:
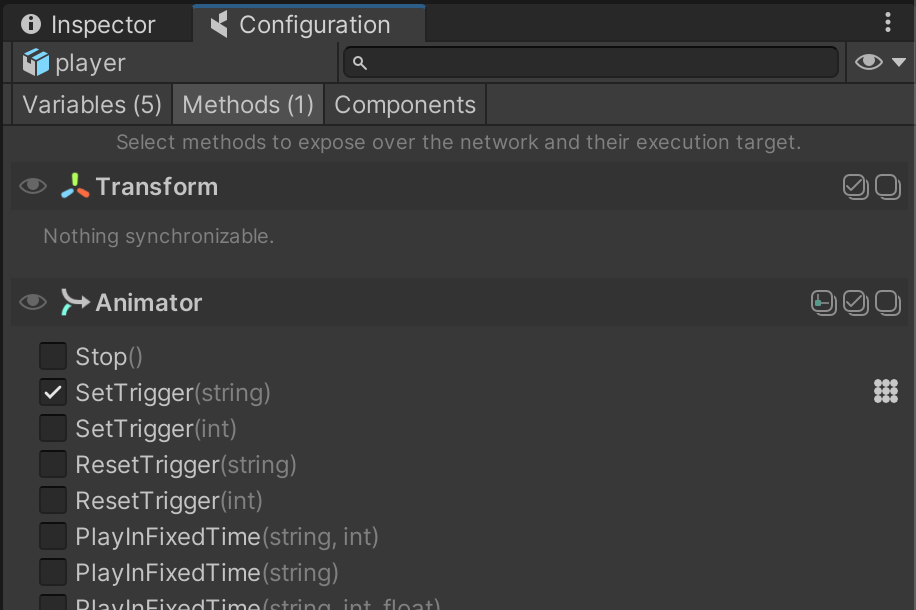
You can see how the method Animator.SetTrigger(string) has been marked as a Network Command. With this done, it is now possible to invoke it over the network using code.
You can find the code doing so in the Wave class (located in /Scripts/Player/Wave.cs):
Analysing this line of code, we can recognize 5 key parts:
First, notice how the command is invoked on a specific
CoherenceSync(thatsyncproperty).We want to invoke this command on a component that is an
Animator.We invoke a method called "Animator.SetTrigger".
With
MessageTarget.Other, we are asking to send this message only to network entities other than the one that has theCoherenceSyncwe chose to use.We pass the string
"Wave"as the first parameter of the method to invoke.
Because we don't invoke this on the one with authority, you will notice that just before invoking the Network Command, we also call SetTrigger locally in the usual way:
An alternative to this would have been to call CoherenceSync.SendCommand() with MessageTarget.All.
In this example we used Network Commands to trigger a transition in an animation state machine, but they can be used to call any instantaneous behavior that has to be replicated over the network. As an example of this, it is also used in the Persistence lesson to change a number in a UI element across all Clients.
Was this helpful?

