3. Areas of interest
Getting updates about every entity in the whole scene is unfeasible for big-world games, like MMOs. For this, coherence has a flexible system for creating areas of interest, and getting updates only about the entities that each Client cares about, using a tool called Live Query.
WASD or Left stick: Move character
Hold Shift or Shoulder button left: Run
Spacebar or Joypad button down: Jump
In this scene
This scene contains two cubes that represent areas of interest. Every connected Client can only see other players if they are standing inside one of these cubes.

How it's set up
Select one of the two GameObjects named LiveQuery. You will see they have a CoherenceLiveQuery component:
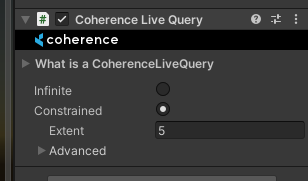
This component defines an area of interest, in this case a 10x10x10 cube (5 is the Extent). This is telling the Replication Server that this Clients is only interested in network entities that are physically present within this volume.
If a Client has to know about the whole world, it's just enough to set the Live Query to Infinite
Now it's clear why Transform.position cannot be excluded from synchronization, as we saw in the first lesson. coherence needs to know where network entities are in space at all times, to detect if they fall within a Live Query or not.
In addition, Live Queries can be moved in space. They can be parented to the camera, to the player, or to other moving elements that denote an area of interest - depending on the type of game.
It is also possible, like in this scene, to have more than one Live Query. They will act as additive, requesting updates from entities that are within at least one of the volumes.
Notice that at least one Live Query is needed: a Client with no Live Query in the scene will receive no updates at all.
If you explored previous scenes you might have noticed that GameObjects with a Live Query component were actually there, but in this scene we gave them a special visual representation, just for demo purposes.
Not just visibility
Try moving in and out of volumes. You will notice that network-instantiation takes care of destroying the GameObject representing a remote entity that exits a Live Query, and reinstantiates it when it enters one again.
Also, notice that the player belonging to the local Client doesn't disappear. coherence will stop sending updates about this instance to other Clients, but the instance is not destroyed locally, as long as the Client retains authority on it.
If a GameObject can be in a state that needs to be computed somehow, it might not appear correctly in the instant it gets recreated.
For instance, an animation state machine might not be in the correct animation state if it had previously reached that state via a trigger parameter. You would have to ensure that the trigger is called again when the instance gets network-instantiated (via a Network Command) or switch your state machine to use other type of animation parameters, which would be automatically synced as soon as the entity gets reinstantiated.
Last updated
Was this helpful?

