Client Connections
Communication between Clients
Overview
ClientConnections are CoherenceSyncs that the CoherenceBridge can handle for you and that let you uniquely identify users connected, find them by their ID, and easily send commands between those users.
When using ClientConnections, CoherenceBridge will spawn a CoherenceSync for each connection (Client or Simulator). Those CoherenceSyncs are subject to a different ruleset than standard CoherenceSyncs:
They can't be created or destroyed by the Client - they are always driven by
CoherenceBridge.They are global - they are replicated across Clients regardless of the Live Query extent.
ClientConnections shine whenever there's a need to communicate something to all the connected players. Usage examples:
Global chat
Game state changes: game started, game ended, map changed
Server announcements
Server-wide leaderboard
Server-wide events
Enabling ClientConnections
The global nature of ClientConnections doesn't fit all game types - for example, it rarely makes sense to keep every Client informed about the presence of all players on the server in an MMORPG. If this is your use case, don't set ClientConnections on your CoherenceBridge.
To enable ClientConnections, turn Global Query on in your CoherenceBridge (it should be on by default):
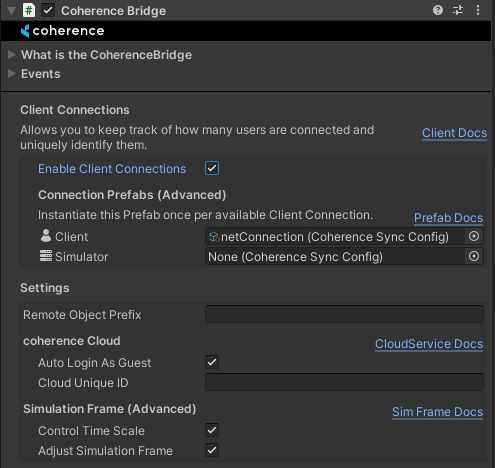
Disabling Global Query on one Client doesn't affect other Clients, i.e. the ClientConnection object of this Client will still be visible to other Clients that have Global Query turned on.
Connection management
Most of the ClientConnection functionality is accessible through the CoherenceBridge.ClientConnections object:
Each connection is represented by a plain C# CoherenceClientConnection object. It contains all the important information about a connection - its ClientID, Type, whether it IsMyConnection, and a reference to the GameObject and CoherenceSync associated with it.
The CoherenceClientConnection.ClientID is guaranteed to not change during a connection's lifetime. However, if a Client disconnects and then connects again to the same Room/World, a new ClientID will be assigned (since a new connection was established).
ClientConnection objects
Each ClientConnection can have a CoherenceSync automatically being spawned and associated with it. Those objects, like any other objects with CoherenceSync, can be used for syncing properties or sending messages, with a little twist - they are global and thus not limited by the CoherenceLiveQuery extent. That makes them perfect candidates for operations like:
Syncing global information - name, stats, tags, etc.
Sending global messages - chat, server interaction
To enable connection objects:
1. Create a ClientConnection Prefab
This step is described in detail in the Prefab setup section. In short, it is enough to create a Prefab with a CoherenceSync and a custom component (PlayerConnection in this example):

2. Link a ClientConnection Prefab to the CoherenceBridge
CoherenceBridgeFor the system to know which object to create for every new Client connection, we have to link our Prefab to the CoherenceBridge. Simply drag the prefab to the Client field in the inspector:
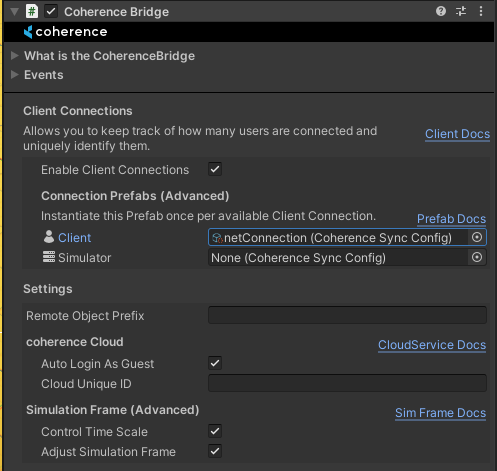
From now on every new connection will be assigned an instance of this Prefab, which can be accessed through the CoherenceClientConnection.GameObject property.
Prefab selection
Note that there's a separate field for the Simulator Connection Prefab. It can be used to spawn a completely different object for the Simulator connection that may contain Simulator-specific commands and replicated properties. If the field is left empty, no object will be created for the Simulator connection.
The Prefab selection process can be also controlled from code using the CoherenceBridge.ClientConnections.ProvidePrefab callback:
A Prefab provided through the ProvidePrefab callback takes precedence over Prefabs linked in the Inspector.
Client messages
Client messages is a shortcut to send Network Commands using a CoherenceClientConnection object as the target instead instead of a CoherenceSync. The end recipient of the command will however still be the CoherenceSync associated with the ClientConnection Prefab, just like a regular Network Command.
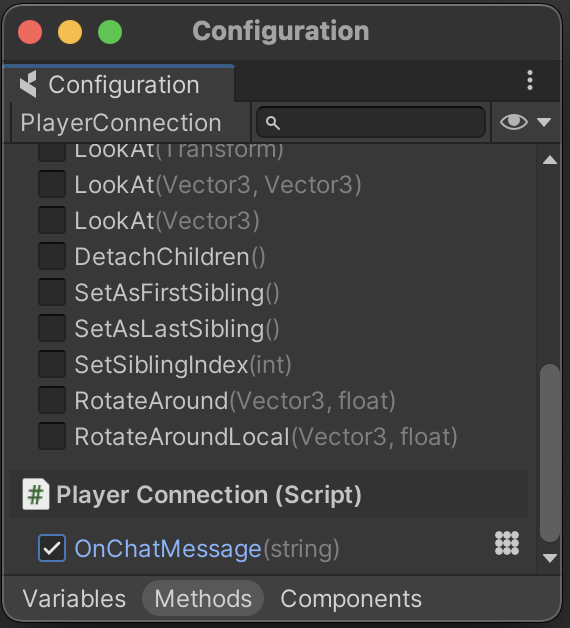
Preparing to use Client messages requires the same approach as exposing a command on a script present on the Client Connection Prefab that we set up in the CoherenceBridge in the previous section:
Don't forget to bind the method to define a Command:
That same Command can now be sent using the CoherenceClientConnection.SendClientMessage method:
If the ClientID of the message recipient is known we can use the CoherenceBridge.ClientConnections directly to send a Client message:
Was this helpful?

