Steam Relay
Steam offers a free networking service for games available on its platform. In order to use Steam Networking you'll need a registered Steam application with a valid Steam App ID. Once you have a Steam App ID, you'll be able to pass messages between clients via Steam's servers.
To make things easy, coherence provides a complete Steam Relay implementation that provides out-of-the-box networking over Steam. The Steam Relay utilizes the Facepunch.Steamworks library to access the Steam API.
The sample code also demonstrates how to register a lobby with the Steam Matchmaking API to make it easy for players to find and join an ongoing session.
The Steam relay is available here: https://github.com/coherence/steam-integration-sample.
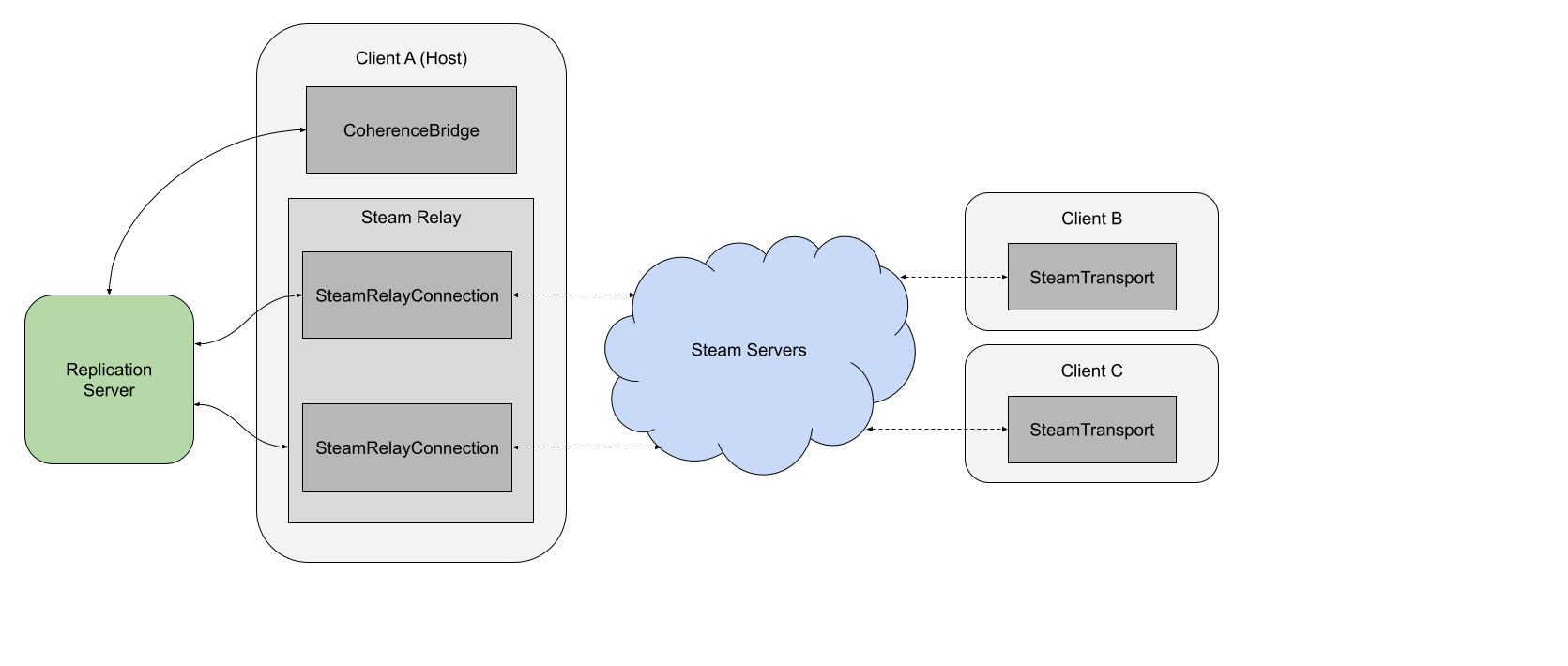
Connecting over Steam, step-by-step
The host (Client A) starts a Replication Server on its local machine.
The host connects to the local Replication Server.
The host initializes a SteamRelay that listens for incoming Steam connections.
Another player (Client B) connects to the host via Steam using the SteamTransport.
The SteamRelay accepts the incoming connection, creating a SteamRelayConnection.
The SteamRelayConnection immediately starts passing data between the Steam servers and the Replication Server.
The relayed connection is now fully established. All data between Client B and the Replication Server is relayed through Steam.
For each new Client that connects, steps 4-7 are repeated.
Although the diagram above shows that traffic is routed via Steam servers, it is often the case that traffic can flow directly between player and host machines without actually making the extra hop via the Steam servers. This technique is commonly referred to as "hole punching" or "NAT Punch-through" and greatly reduces latency, however, it is not supported on all networks due to firewall restrictions.
Steam's networking service will first attempt a NAT punch-through and then automatically fall back to relayed communication if the punch-through failed.
To be able to test your game with the Steam Relay you'll need at least two Steam accounts - even for local development. Since only a single Steam account can be logged in to one machine at a time, you will need at least two machines or a sandbox solution to be able to connect. Trying to connect two instances of the game on the same machine will result in "invalid connection" or "failed to create lobby" errors.
Last updated
Was this helpful?

