Syncing child GameObjects
Binding to variables and methods within the hierarchy
If a synced Prefab has a hierarchy, you can synchronize variables, methods and component actions for any of the child GameObjects within its hierarchy.
Note: on this page we cover children GameObjects or nested Prefabs that don't have their ownCoherenceSync.
If a child object has a CoherenceSync of their own, they become an independent network entity. For that, see the Parenting section.
When the Configure window is open it will show the variables, methods and component actions available for synchronization for your currently selected GameObject.
First, make sure to be editing the Prefab in Prefab Mode:
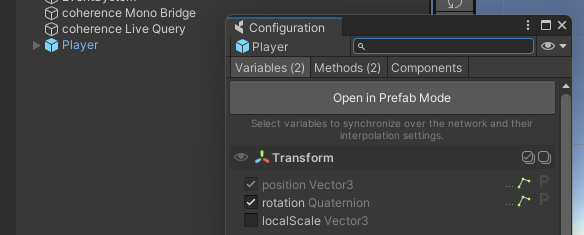
Once in Prefab Mode and with the Configure window open, shift the selection to any of the GameObjects that belong to the hierarchy.
The Configure window will be updated automatically, showing you everything that is available to be synchronized on the child GameObject:
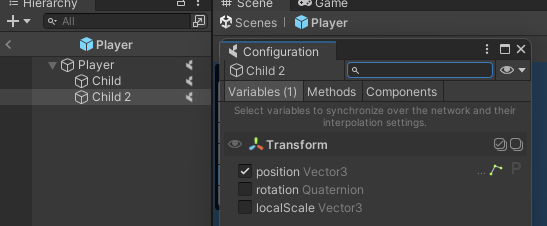
That's it!
Syncing properties, methods and component actions on child GameObjects doesn't require any different flow than what you usually do for the root object. They all get collected and networked as part of one single network entity.
After your changes to GameObject, don't forget to Bake again to rebuild the netcode for the entity.
Make sure to not destroy child GameObjects that have synced properties, or you will receive a warning in the Console. To destroy a synced object, always remove the root.
(you can totally destroy children that don't have any synced property)
Last updated
Was this helpful?

