Continuous Integration
Tips and trips for setting up Continuous Integration (CI) for your projects
Tips for automated building
public static void GenerateSchema() { BakeUtil.GenerateSchema(out var _, out var _); }public static void Bake() { BakeUtil.Bake(BakeUtil.Settings.Default); }
Uploading schemas in CI scenarios
Simulator build pipeline
Building and uploading to the Cloud
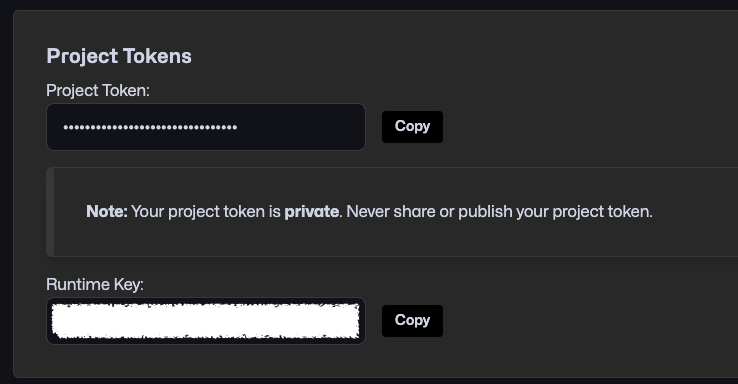
Project Token
Commands example
Customizing your Simulator builds
Was this helpful?

