Authority transfer
Authority over an entity is transferrable, so it is possible to move the authority between different Clients or even to a Simulator. This is useful for things such as balancing the simulation load, or for exchanging items. It is possible for an entity to have no Client or Simulator as the authority - these entities are considered orphaned and are not simulated.
Types of authority transfer
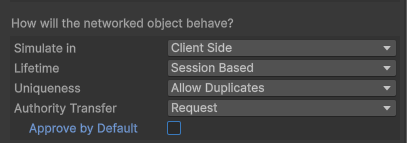
In the design phase, CoherenceSync objects can be configured to handle authority transfer in different ways:
Request. Authority transfer may be requested, but it may be rejected by the current authority.
Steal. Authority will always be given to the requesting party on a FCFS ("first come first serve") basis.
Not transferable. Authority cannot be transferred.
Using the Not transferable option will also disable giving the authority to other Clients, even if you own the entity.
If you want to instantiate entities on the host or Simulator and then transfer the authority to a Client, it is recommended to use the Request option, with Approve by Default set to false.
When using the Request mode, you can use CoherenceSync.OnAuthorityRequest to decide which transfers should go through.
Auto-adopt Orphan
When Lifetime is set to Persistent, you will see an extra checkbox called Auto-adopt Orphan.
Enabling this option makes it so that if an entity is abandoned by its owner, the Replication Server will assign it to a Client again, as soon as possible. For instance, this can be useful in a big game world, where entities often go out of LiveQueries. When they are first seen again by a Client, the Auto-adopt Orphan option ensures that the Client takes over that entity (i.e. its State authority) without you having to write code for it.
Note: If you abandon an entity but it's still in your LiveQuery, on the next frame the Replication Server might assign it to you again. If you want more control over that, then perhaps you should turn Auto-adopt Orphan off, and implement callbacks to the authority events for that entity.
Requesting authority in code
Requesting authority is very straightforward.
RequestAuthorityAsync returns a result with Type Success if the request was successful, or one of the result listed below if it was not:
Canceled: either the networked entity was destroyed while the request was in progress, or a custom CancellationToken was passed to the method and used to cancel the request before it completed.
Entity Not Synchronized With Network: the entity is not being networked (its CoherenceBridge is not connected to a room or a world).
Entity Orphaned Error: the entity is orphaned, in which case you must call
CoherenceSync.Adoptinstead to request authority.Entity Not Transferable Error: the entity is not allowed to be transferred because its
Authority Transferhas been set toNon Transferable.Request Rejected Error: this can happen if
Authority Transferhas been set toRequestand the client or server that holds authority over the entity rejected the request.Already Has Authority Error: the client already has the requested authority over the entity.
Invalid Authority Type Error: the requested authority type is not supported. This can happen if a request is made to acquire authority of type
None.CoherenceSync.AbandonAuthoritycan be used to give up authority (orphaning the entity) instead.Entity Is Client Connection Error: the entity is created by the Client Connection for the client making the authority request.
Timeout Error: the request was not approved or rejected by the server within 10 seconds. This is fail-safe so that the request is always guaranteed to complete.
Because of the asynchronous nature of the authority request, clients can receive commands for entities that they no longer have authority over. Such commands are dropped.
In addition to awaiting Task<RequestAuthorityResult> returned by CoherenceSync.RequestAuthorityAsync, you can also get notified about authority requests being made (OnAuthorityRequest), authority requests being rejected (OnAuthorityRequestRejected), and state or input authority being acquired (OnStateAuthority / OnInputAuthority) or lost (OnStateRemote / OnInputRemote) via UnityEvents on the CoherenceSync.
Last updated
Was this helpful?

